Algorithm efficiency
Objective
- discuss the order of complexity of algorithms
Algorithm efficiency (Order)
- Cprogramming.com
article on the order of algorithms
- big O notation: a measure of algorithm efficiency which describes relatively
how much time will be taken to complete the algorithm related to the size of the data set
- if the order of algorithm A is n2 and the order of algorithm B
is n log n, there are implications:
- log n in computer caculations is usually base 2 log, but that detail doesn't matter
for ordinary comparisons of algorithm complexity
- when the number of data items (n) is small, the difference in the order of the algorithms
probably won't matter much since other efficiencies and overhead will probably have
an even greater effect than the order
- for large data sets (large n), algorithm B has a distinct advantage
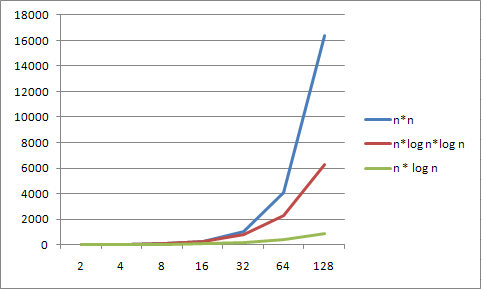
- estimated relative runtimes:
| n | Alg A runtime | Alg B runtime |
|---|
| 10 | 100 | 33 |
| 100 | 10,000 | 664 |
| 1,000 | 1,000,000 | 9,966 |
| 10,000 | 100,000,000 | 132,877 |
| 100,000 | 10,000,000,000 | 1,660,964 |
| 1,000,000 | 1,000,000,000,000 | 19,931,569 |
- for small data sets, the increase in algorithm complexity which is often needed to
achieve a better algorithm order may not be worth the effort - it may depend on how
often the containing application is run
- if you find some algorithms with their order specified, here is a list of
common orders from best to worst
- 1
- log n
- n
- n log n
- nc (where n2 beats n3 beats n4, etc.)
- an (where 2n beats 3n beats 4n, etc.)
- N! (factorial)
- Nn
Graphic example of order growth